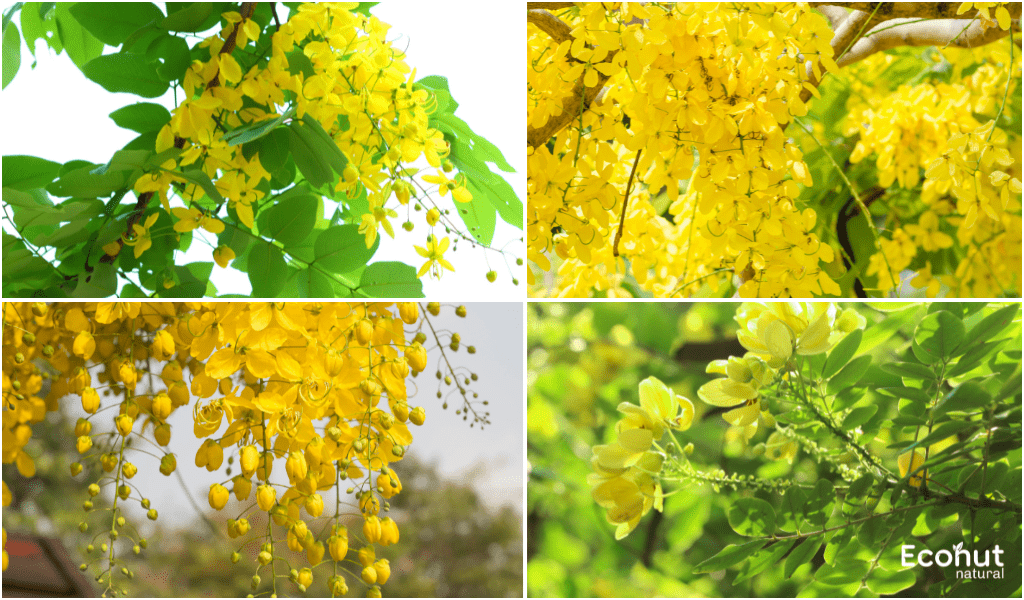
Amaltas (Cassia Fistula) is an Ayurvedic plant that is considered exceedingly remarkable and is recognized for its ability to kill sickness from the roots. Because of its many therapeutic benefits, this plant’s fruit pulp, seeds, leaves, and roots are used to treat a variety of illnesses.
The plant known by the botanical name Cassia fistula is primarily native to India and Pakistan, but it is also widely disturbed in many other tropical regions, such as Mexico, Ecuador, the West Indies, Belize, Australia, and Brazil, as well as in various parts of South-east Asia, Thailand, China, South Africa, Costa Rica, and Guyana. The Amaltas flower is recognized as the state flower of Kerala and the national flower of Thailand because of its vivid yellow blooms.
Description
Amaltas tree can grow up to 60 feet in height, with a trunk diameter of roughly 0.5 meters. This plant has alternate, pinnate leaves that are 15-20 cm long and have two pairs of 4–8 leaflets. Fruits are cylinder-shaped pods that hold two to five seeds each. These are green pods that turn a dark brownish color when they mature. The seeds have a glossy black color. Beautiful bunches of yellow flowers adorn this shrub.
Botanical Name:
Cassia Fistula
Family:
Fabaceae
Leaves:
The lovely, fluffy leaves of the Amaltas tree are deciduous, meaning they fall off in the fall. These leaves are pinnate, meaning that many leaflets are placed on either side of a central stem. Three to eight pairs of oval-shaped, pointy leaflets can be found on each Amaltas leaf. The leaflets have a smooth, lighter-colored underside and a smooth, green top.
Flowers:
The Amaltas tree is also called the “Golden Shower Tree” because of its breathtaking golden yellow blossoms. Racemes are the big, drooping clusters of flowers that these blooms bloom in. Five vibrant yellow petals, roughly equal in size and shape, are grouped in a bell-shaped pattern on each flower. The flowers put on a magnificent show during their spring and summer blooms.
Bark:
Amaltas its bark is smooth and light gray. The bark of the tree gets darker brown and coarser as it ages.
Habitat:
Amaltas is primarily indigenous to Pakistan and India, while it is also found in several other regions of Southeast Asia. Additionally, South Africa, Brazil, Thailand, and China distribute it. Thailand’s national flower is the amaltas flower, which grows on the national tree. India is home to the cultivation of this plant for both traditional and medical use.
Parts Used:
- Leaf
- Root
- Fruit
- Bark
- Flower
Dosage:
- Fruit Pulp – 5-10gm
- Root Bark – 50-100ml
- For Purgation – 10-20gm
- Flowers – 5-10gm
Chemical Constituents
This plant’s fruits stem bark, and leaves are rich in biologically active substances with a range of therapeutic uses, including anthraquinones, flavonoids, and derivatives of flavon-3-ol, alkaloids, glycosides, tannin, saponin, terpenoids, reducing sugar, and steroids.
Synonyms in the Sanskrit language
Deerghaphala – Have long fruit
Svaranabhushana – Having golden yellow colored flowers
Chaturangula – Fruits having four fingers length
Shampaka – It is Auspicious
Arevata – Has detoxifying properties
Other Language Names of Amaltas (Cassia Fistula)
Malayalam name – Kanikonna
Hindi name – Amaltas
Sanskrit name – Shampaka, Suvarnaka, Swarnabhushan, Aragvadha
Punjabi name – Girdanali
Telugu name – Rela
Bengali name – Sondal
Farsi name – Khiyar
English name – Purging cassia
Tamil name – Kondrem
Kannada name – Phalus
Marathi name – Bahva
Gujarati name – Garmalo
Arabic name – Kattan
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Class | Dicotyledons |
| Subclass | Polypetalae |
| Series | Thalamiflorae |
| Order | Parietales |
| Family | Fabaceae |
| Genus | Cassia |
| Species | Fistula |
Ayurvedic Properties
Hindi/Sanskrit
- Rasa -Madhur
- Guna -Mridu,Guru,Singdha
- Virya -Sheet
- Vipaka -Madhur
English
- Taste -Sweet
- Physical Property-Soft,Heavy,Unctuous
- Potency- Cold
- Metabolic Property (After Digestion)-Sweet
Amaltas (Cassia Fistula) Uses
For Skin Disease:
Amaltas leaves can be used to treat eruptions, ringworms, and eczema on the skin. The fruit pulp has demonstrated promise in treating skin conditions and worms, while the root may help with dermatological difficulties.
For Suppressing Cough:
Amaltas pods can be burned, ashed, and mixed with salt and honey to potentially relieve coughs. It is thought to have antitussive qualities. There may be some efficacy to this combo in treating fevers as well. It’s also been stated that Amaltas leaves can relieve coughing.
For Constipation:
One popular method for treating constipation is to combine Amaltas pulp with hot water and drink it.
Amaltas (Cassia Fistula) Benefits
Bolsters Immunity:
Amaltas formulation provides a number of traditional medicines for enhancing the immune system, combating germs, and protecting the body against various infections because it contains antioxidants and ascorbic acid. Amaltas (Cassia Fistula) also exhibits potent anti-viral, anti-bacterial, and antifungal qualities, making it a highly useful remedy for infections such as fever, colds, sore throats, and other respiratory disorders.
Promotes Digestion:
The process of digestion is essential to our ability to absorb nutrients from the food we eat. Unfortunately, intestinal pain is a common side effect of the modern diet, which heavily relies on processed and quick foods. Fortunately, a number of natural treatments are available to support effective and seamless digestion. For example, including items like fennel, ginger, and peppermint in your diet can help ease digestive discomforts like cramping and bloating.
Prevents Infections:
Since ancient times, the collection of biological substances found in this herb has been utilized to combat bacteria and protect the body from a variety of illnesses. Amaltas is used to cure and heal wounds in addition to eliminating bacteria and germs from the body because of its potent anti-microbial qualities.
Diabetes:
Strong hypoglycemic properties conferred by amaltas are crucial for regulating the body’s blood sugar levels. When amaltas syrup is consumed, the β-pancreatic cells, which aid in the synthesis of insulin, become highly active. Additionally, it aids in lowering the rate at which starch is converted to glucose, lowering blood glucose levels and maintaining a healthy diabetic reading.
Don’t miss: Brihati, Poison Berry (Solanum indicum) – Uses, Benefites, Dosage & Side Effects
Amaltas (Cassia Fistula) Side Effects
Skin Irritation:
Some persons may become irritated when Amaltas paste is applied topically to injured skin or over an extended length of time. It is preferable to combine the Amaltas paste with oil or honey before applying it if you have sensitive skin.
Stomach cramps:
Particularly for those with sensitive stomachs, amaltas might aggravate the digestive tract and result in cramping in the stomach.
Excessive Diarrhea:
Amaltas contains anthraquinones, which give it powerful laxative qualities. Overdosing on Amaltas or using it for prolonged periods of time might cause electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, and severe diarrhea.
Interaction with Medications:
Certain drugs, including blood thinners, diuretics, and diabetes medications, may interact with amaltas. Before using Amaltas, it’s crucial to speak with your doctor if you take any drugs.
Conclusion
Amaltas, often known as the “Golden Shower Tree,” is endowed with numerous health advantages. Owing to the beneficial effects of the vital bio-active elements, it is frequently used to treat feverish and flu-like illnesses, cough, colds, sore throats, digestive abnormalities, improve heart function, prevent skin infections, aid in digestion, and many other disorders.
FAQS
What Are Amaltas’s Medicinal Properties?
With properties that include being antidiabetic, hepatoprotective (protecting the liver), antitussive, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, antitumor, anti-itching, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic, larvicidal antioxidant, antileishmanial, and wound healing, amaltas is an incredibly helpful ayurvedic plant.
Is Amaltas Fruit Beneficial for Treating Pain in the Abdomen?
Amaltas possesses potent anti-inflammatory qualities. Abdominal pain can be quickly relieved by applying a paste prepared from the Amaltas fruit peel around the navel region. It is also used to treat other conditions like GERD, gastritis, indigestion, and bloating.
What is the family of Amaltas?
Fabaceae
What is Amaltas used for?
For skin ailments like ringworms, eczema, and skin eruptions, amaltas leaves can be utilized. Amaltas root may be beneficial for skin issues. It has also been discovered that Amaltas fruit pulp is useful in the treatment of worms and skin conditions. You can use amaltas leaves for erysipelas.